5.13. Configuring Your DHCP Server
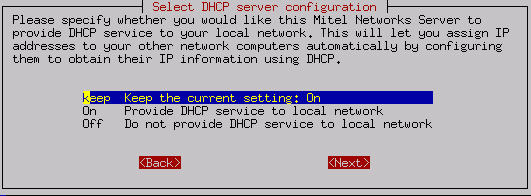
You now will be prompted regarding DHCP service. Your SME Server can be configured to provide DHCP service to your internal network. The DHCP server can automatically configure the other computers on your internal network with such parameters as non-routable IP address, subnet mask and gateway IP address. This reduces the risk of error and simplifies the process of configuring your network.
We recommend configuring your server to use DHCP to configure all of your network clients. You should not do this if there is an existing DHCP server on your network as there should typically be only one DHCP server per network.
5.13.1. Configuring the DHCP Address Range
Before the DHCP server is able to assign IP addresses to the computers on your network, you need to tell it what range of IP addresses it can safely distribute. As above, this section is pre-configured with defaults that are appropriate in most situations. If you have fewer than 180 machines on your local network and no reason to prefer one range of IP addresses over another, you can simply accept the defaults for these screens.
If the defaults are not appropriate to your situation, you may need a bit of background to understand how to configure this range. For example, if you entered the server address of 192.168.1.1 and subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 (the default settings), the configuration script will infer that your "network" is 192.168.1.0 and that valid addresses are from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254. If you entered some number such as 192.168.100.1 for the server, the script will infer that your valid addresses will be 192.168.100.1 through 192.168.100.254.
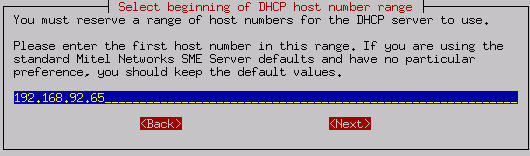
If you enter the number " 192.168.202.65 " as the "beginning of DHCP address range", as shown below, the first computer served by the DHCP server would receive the IP address of 192.168.202.65. The second computer would receive the IP address of 192.168.1. 66, and so on.
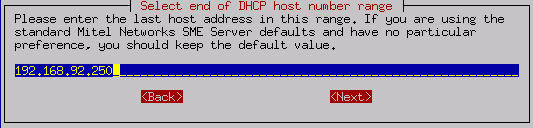
If you specify that the end of the range is " 192.168.202.250 ", as shown below, then the last computer able to receive DHCP service would be assigned the IP address 192.168.202.250. Once all the available IP addresses within that range are assigned, your DHCP server will no longer serve IP addresses to new computers.
5.13.2. Important issues about the DHCP address range
The usual range maximum is 254: Normally the "end of DHCP address range" cannot exceed "254". If you have more than 253 computers on your network and would like to exceed this range maximum, you can use a Class B or Class A non-routable address for your network. In this case the number entered in the "end of range" field needs to be calculated and entered a little differently. Note that the default range maximum is 250. As explained below, this is to allow a few static addresses at the end of the range.
The local IP address assigned to your server itself must fall outside of this range: In other words, you should not assign your server a non-routable IP address that is also assignable by the DHCP service to another computer on your network. If your server is assigned the IP address of "192.168.1.1" then the lowest possible number in the DHCP range should be "2".
We recommend that you leave a small pool of IP addresses that can be manually assigned: Some of the computers (or devices such as network printers) on your network may not be able to accept DHCP service. Therefore, it is preferable to exclude some IP addresses from the DHCP range so they are available to be assigned manually to those computers. For example, using the 192.168.1.0 block of addresses, the default "beginning of DHCP address range" is "192.168.1.65". This ensures that non-routable IP addresses "192.168.1. 2 " through "192.168.1. 64 " are available to you if any computers on your network cannot accept DHCP service. Additionally, the default end of "192.168.1.250" leaves addresses "192.168.1. 251 " through "192.168.1. 254 " available.