11.1. Remote Access
- 11.1.1. ssh
-
- 11.1.1.1. ssh clients for Windows and Macintosh
- 11.1.2. PPTP
- 11.1.3. FTP
- 11.1.4. telnet
If you're an advanced user, the SME Server provides several different ways to access the underlying operating system, either from a computer on your internal network or from a computer outside your site on the Internet. Additionally, you have the ability to access your computer network securely from a remote computer. All of these operations are configured from the screen shown below in the server manager.
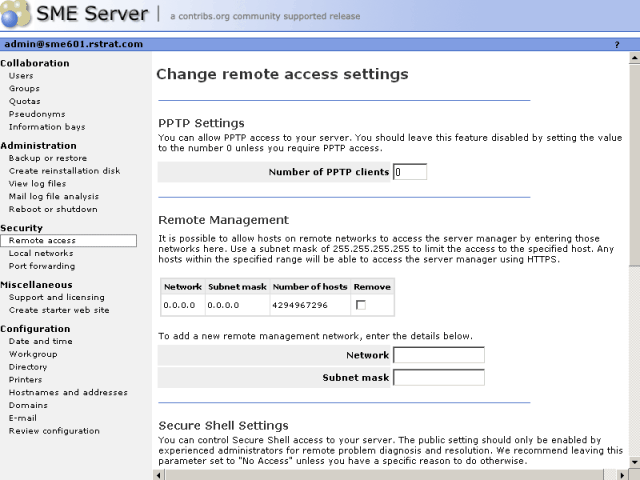
Each of these remote access methods is described below.
11.1.1. ssh
If you need to connect directly to your server and login from a remote system belonging to you, we strongly encourage you to use ssh instead of telnet. In addition to UNIX and Linux systems, ssh client software is now also available for Windows and Macintosh systems. (See the section below.)
If you do not have any reason to allow remote access, we suggest you set this to No access.
Once ssh is enabled, you should be able to connect to your server simply by launching the ssh client on your remote system and ensuring that it is pointed to the external domain name or IP address for your server. In the default configuration, you should next be prompted for your user name. After you enter admin and your administrative password, you will be in the server console. From here you can change the server configuration, access the server manager through a text browser or perform other server console tasks.
If you do enable ssh access, you have two additional configuration options:
-
Allow administrative command line access over ssh - This allows someone to connect to your server and login as "root" with the administrative password. The user would then have full access to the underlying operating system. This can be useful if someone is providing remote support for your system, but in most cases we recommend setting this to No .
-
Allow ssh using standard passwords - If you choose Yes (the default), users will be able to connect to the server using a standard user name and password. This may be a concern from a security point of view, in that someone wishing to break into your system could connect to your ssh server and repeatedly enter user names and passwords in an attempt to find a valid combination. A more secure way to allow ssh access is called RSA Authentication and involves the copying of an ssh key from the client to the server. This method is supported by your server, but is beyond the scope of this user guide and will eventually be covered by additional documentation on the contribs.org web site.
| Note | |
|---|---|
|
By default, only two user names can be used to login remotely to the server: admin (to access the server console) and root (to use the Linux shell). Regular users are not permitted to login to the server itself. If you give another user the ability to login remotely to the server, you will need to access the underlying Linux operating system and manually change the user's shell in /etc/passwd. |
11.1.1.1. ssh clients for Windows and Macintosh systems
A number of different free software programs provide ssh clients for use in a Windows or Macintosh environment. Several are extensions of existing telnet programs that include ssh functionality. Two different lists of known clients can be found online at http://www.openssh.com/windows.html and http://www.freessh.org/.
A commercial ssh client is available from SSH Communications Security at: http://www.ssh.com/products/ssh/download.html. Note that the client is free for evaluation, academic and certain non-commercial uses.
11.1.2. PPTP
The Point-to-Point Tunnelling Protocol (PPTP) is used to create client-to-server Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and was developed by the PPTP Forum, an industry group which included Microsoft and several other companies. A VPN is a private network of computers that uses the public Internet to connect some nodes. PPTP allows users to connect to their corporate networks across the Internet.
Microsoft's PPTP implementation is widely used in the Windows world to provide remote access across the Internet. If you have a remote Windows system (for instance, a laptop or a home computer) that has access to the Internet, you can also access the information stored on your server.
If you wish to enable VPN access, you must decide how many individual PPTP clients you will allow to connect to your server simultaneously, and enter that number here. The simplest method is to enter the total number of remote PPTP clients in your organization. Alternatively, if you have a slow connection to the Internet and do not want all of those PPTP clients to connect at the same time, you can enter a lower number here. For instance, if you have five users who from time to time use PPTP to connect remotely, entering 5 here would allow all of them to connect at any time. Entering 2 would only allow two users to connect at any given time. If a third user tried to connect, he or she would receive an error message and would not be able to connect until one of the other users disconnected. If, on the other hand, you entered 0, no PPTP connections would be allowed.
After you enter a number and press Save, the server should be ready to accept PPTP connections.
To connect using PPTP, the protocol must be installed on each remote Windows client. Typically, this is done through the Network Control Panel (you may need to have your original Windows installation CD available). After it is installed (a reboot of your Windows system may be needed), you can create new connections through the Dial-Up Networking panel by entering the external IP address of the server you wish to connect to. Once you're finished, you should be able to initiate a PPTP connection by double-clicking the appropriate icon in the Dial-Up Networking window. When you then open up your Network Neighborhood window, you should see your server workgroup listed there.
| Note | |
|---|---|
|
Your connection to the Internet needs to be established first before you initiate the PPTP connection. This may involve double-clicking one Dial-Up Networking icon to start your Internet connection, then double-clicking a second icon to start the PPTP connection. To shut down, disconnect your PPTP connection first, then disconnect from your ISP. |
| Warning | |
|---|---|
|
To protect your network, the SME Server enforces the use of 128-bit encryption for PPTP connections, rather than the 40-bit encryption provided in earlier versions of Microsoft's PPTP software. If you are unable to establish a PPTP connection to your server, you should visit http://windowsupdate.microsoft.com/ and download the appropriate update. Due to the dynamic nature of Microsoft's web site, the page may appear differently depending upon the version of Windows you are using. In most cases, you will want to look or search for Virtual Private Networking or a Dial Up Networking 128-bit encryption update . You may need to install the 40-bit encryption update first, and then install the 128-bit encryption update. Note that with Microsoft's ActiveUpdate process, if you are not presented with the choice for this update, it is most likely already installed in your system. |
11.1.3. FTP
Another way to upload or download files to and from yourserver is to enable a protocol called FTP, or "file transfer protocol". This screen enables you to set your policy for FTP. Note that allowing liberal FTP access to your server does reduce your security. You have two options that you can set here.
FTP user account access: Private FTP access allows only people on your internal network to write files to your server. Public FTP access allows users both inside and outside your local network to read or write files on your server, provided they have an account and password. If, for example, you want to be able to update your web site from home using FTP, you would choose the "Public" setting. We strongly recommend you leave this as Private unless you have a specific reason to do so.
FTP access limits: This allows you to set an overall site-wide policy for FTP access. The setting you choose here will override all other FTP settings on your server . For example, if you choose "Disable public FTP access" here and then later configure an i-bay to allow public FTP access from the Internet, such access will be forbidden. Note that one of the choices here allows you to completely disable any use of FTP.
11.1.4. telnet
telnet has traditionally been one of the tools used to login remotely to other systems across a network or the Internet. Telnet can be useful in that it allows you to login remotely and diagnose problems or configure settings. However, when you use telnet, all user names and passwords are transmitted without any kind of encryption, dramatically reducing the security of your server. For that reason, we strongly recommend the use of ssh as described above.
| Note | |
|---|---|
|
Because ssh usage has increased to an acceptable level, telnet access control has been removed from this Server Manager panel. |